Gantry welding machines are specialized automated welding systems designed for high-precision, large-scale welding applications, particularly in industries such as shipbuilding, structural steel fabrication, and heavy machinery manufacturing. A gantry welding machine operates on a principle of automated movement and precise control of the welding head over a workpiece.
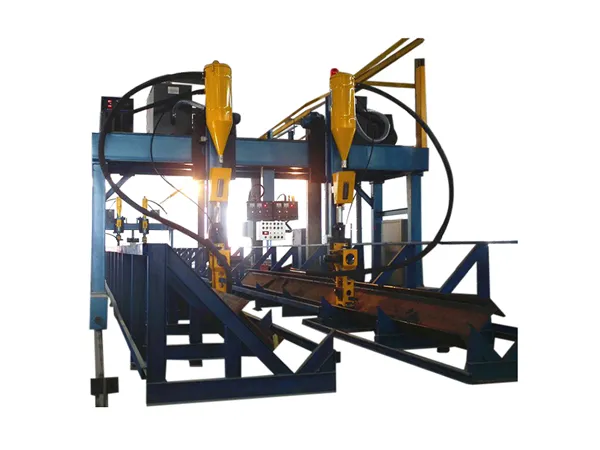

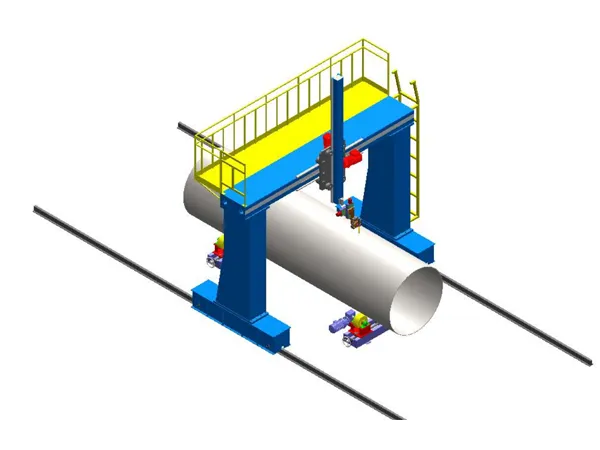
Gantry Structure: The machine features an overhead bridge-like structure (the gantry) that spans the welding area. This gantry provides a stable and rigid framework for the welding process.
Multi-Axis Movement: A carriage or trolley carrying the welding head moves along the gantry (typically the X-axis). The gantry itself can also move along rails (the Y-axis), and the welding head often has vertical movement (the Z-axis). This multi-axis movement allows the welding head to reach any point within the machine's working envelope.
Automated Control System: The movement of the gantry and the welding head is controlled by a sophisticated numerical control (CNC) system or a programmable logic controller (PLC). This system directs servo motors that drive the movement along each axis with high precision.
Welding Process Integration: The gantry system is integrated with various welding power sources and equipment (e.g., Submerged Arc Welding (SAW), Metal Inert Gas (MIG), Metal Active Gas (MAG)). The control system also manages the welding parameters such as voltage, current, wire feed speed, and travel speed.
Seam Tracking (Optional but crucial for precision): Advanced gantry welding machines often incorporate seam tracking systems. These systems use sensors (e.g., mechanical, laser, vision) to detect the actual weld joint in real-time and automatically adjust the welding head position to follow the seam accurately, even if the workpiece has slight variations or distortions.
Material Handling: While not directly part of the welding principle, gantry machines are often integrated with material handling systems (e.g., conveyors, positioners) to move and orient the workpiece efficiently.
Achieving such high welding precision (0.1mm) requires a combination of advanced technologies and meticulous engineering:
High-Precision Motion Control System:
High-Resolution Encoders: Servo motors on each axis must be equipped with high-resolution encoders to provide precise feedback on the welding head's position.
This allows the control system to make minute adjustments to ensure accuracy.
Precision Linear Guides and Ball Screws: The gantry and welding head movements rely on high-quality linear guides and ball screws with minimal backlash. These components ensure smooth, accurate, and repeatable motion.
Advanced Motion Controllers: The CNC or PLC must have sophisticated motion control algorithms that can interpret the desired path and precisely coordinate the movement of all axes, compensating for any dynamic errors.
Real-Time Seam Tracking System:
High-Accuracy Sensors: Implementing a non-contact seam tracking system like laser or vision tracking is essential. These sensors can provide very precise measurements of the weld joint's location and orientation in real-time.
Fast Feedback Loop: The integration between the seam tracking sensor and the motion control system must have a very fast feedback loop. This allows for immediate corrections to the welding head's position in response to any deviations in the weld seam.
Stable and Rigid Machine Structure:
Heavy-Duty Gantry: The gantry structure must be robust and have high rigidity to minimize vibrations and deflections during the welding process. Any movement or instability in the structure will directly impact welding accuracy.
Precision Alignment: The rails and guides on which the gantry and welding head move must be precisely aligned during the machine's assembly and regularly maintained.
Optimized Welding Process and Parameters:
Consistent Welding Parameters: Maintaining very stable and consistent welding parameters (current, voltage, travel speed, wire feed rate, shielding gas flow) is crucial. Fluctuations can lead to variations in the weld bead and affect precision.
Minimized Heat Input and Distortion: Controlling the heat input during welding is vital to minimize thermal distortion of the workpiece. Excessive distortion can make it impossible to maintain 0.1mm accuracy over the entire weld length. Techniques like pulsed welding or optimized welding sequences can help.
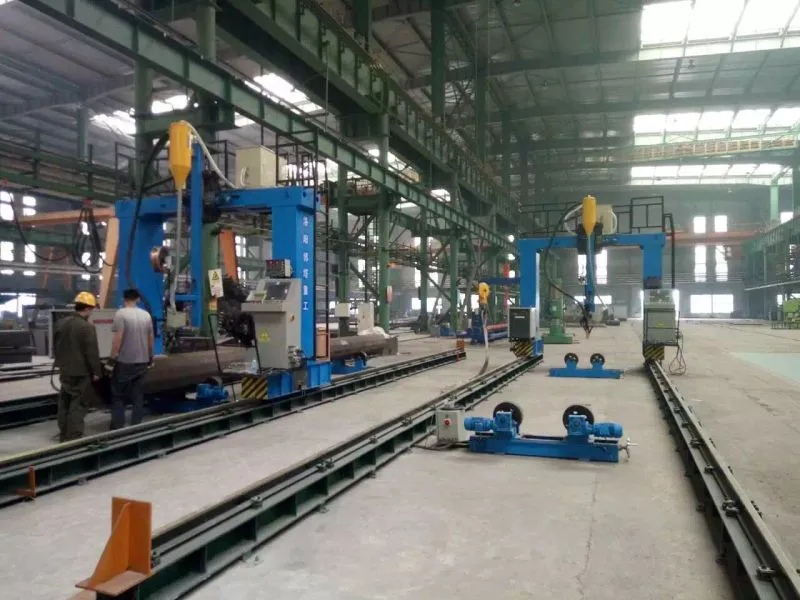

Precise Workpiece Fixturing:
Accurate Clamping: The workpiece must be securely and accurately fixtured to prevent any movement or misalignment during the welding process. The fixturing itself must be designed and manufactured with high precision.
Calibration and Feedback Systems:
Regular Calibration: The entire system, including the motion control, seam tracking, and welding head positioning, must be regularly calibrated using high-precision instruments to ensure accuracy is maintained over time.
Position Feedback Verification: Implementing secondary feedback systems (e.g., linear scales) in addition to motor encoders can provide an extra layer of verification of the welding head's actual position.
In summary, achieving 0.1mm welding precision with a gantry welding machine is a complex task that demands a highly integrated system with precise motion control, real-time seam tracking, a stable mechanical structure, optimized welding processes, and meticulous attention to detail in fixturing and calibration.
No. 1 Intersection of Chuangye Avenue and Weilai Avenue,
Yiyang County,Luoyang City, Henan Province, China
+86 400-0379-069
Copyright © 2023 An Automated Welding and Cutting Equipment Manufacturer Focusing on Welding Column Boom and Welding Rotator | All Rights Reserved Technical support: ShangXian