Customizing a wind tower welding production line involves a comprehensive assessment of your specific manufacturing needs and then selecting and integrating the appropriate automated machinery to meet those requirements. This process is highly specialized and requires a tailored approach rather than a one-size-fits-all solution.

To effectively customize a production line, you must first define your operational goals and constraints. These factors will dictate the design and equipment of your line.
Production Capacity: Determine the number of tower sections or entire towers you need to produce per week, month, or year. This directly influences the required welding speed, material handling capacity, and the overall level of automation.
Tower Specifications: The dimensions and materials of the towers you will produce are critical.
Diameter and Thickness: The range of diameters and steel plate thicknesses you plan to use will determine the size and power of key equipment like plate rolling machines and welding power sources.
Section Length: The standard length of your tower "cans" dictates the required length of welding manipulators and the overall workshop layout.
Material Grade: Different steel grades have unique welding requirements that will influence the choice of welding processes and consumables.
Workshop Layout: The physical space of your facility is a major constraint.
Available Space: Map out your facility to account for the entire production flow, from raw material storage to finished product handling.
Ceiling Height and Crane Capacity: Ensure your overhead cranes can handle the largest and heaviest tower sections.
Material Flow: Design a logical, linear flow to minimize unnecessary handling and movement.
Material Handling Systems:
Automated Loading/Unloading: Implement robotic or gantry systems for efficient movement of tower sections.
Conveyors and Rollers: Customize the size and type of conveyors to handle the dimensions and weight of your specific tower sections.
Positioners and Rotators: Utilize heavy-duty positioners and rotators to allow for optimal welding angles and access.
Fit-Up Stations: Design specialized fit-up stations that ensure precise alignment of tower sections before welding.
Welding Process Optimization:
Welding Method Selection: Choose the most suitable welding processes for wind tower fabrication (e.g., submerged arc welding (SAW), gas metal arc welding (GMAW), flux-cored arc welding (FCAW)).
Automated Welding Carriages: Integrate automated welding carriages that can traverse the tower sections, maintaining consistent speed and arc length.
Multi-Wire Welding: Consider multi-wire SAW systems for increased deposition rates and faster welding.
Narrow Gap Welding: Implement narrow gap welding techniques to reduce weld volume and improve efficiency.
Robotic Welding Cells: For specific, repetitive tasks or complex geometries, robotic welding can offer high precision and repeatability.
Quality Control and Inspection:
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Integrate automated NDT systems (e.g., ultrasonic testing, eddy current testing) directly into the production line to ensure weld integrity.
Vision Systems: Implement vision systems for real-time weld monitoring, defect detection, and precise seam tracking.
Data Logging and Traceability: Establish systems to record welding parameters and inspection results for comprehensive traceability.
Automation and Control Systems:
PLC/HMI Control: Implement a centralized PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) and HMI (Human-Machine Interface) for comprehensive control and monitoring of the entire line.
Robotic Integration: Integrate robots for material handling, welding, grinding, or inspection tasks.
Sensors and Feedback Systems: Utilize sensors to monitor welding parameters, component positioning, and environmental conditions.
Fume Extraction and Safety:
Localized Fume Extraction: Install efficient fume extraction systems at each welding station to ensure a safe working environment.
Safety Guarding and Interlocks: Implement physical barriers, light curtains, and interlocks to prevent accidents.
Emergency Stop Systems: Ensure readily accessible emergency stop buttons throughout the production line.
1) Plate Preparation
This stage involves cutting steel plates to the correct size and preparing their edges for welding.
Equipment:
CNC Plasma/Oxy-fuel Cutting Machine: Used to precisely cut the large steel plates. Customization can include adding plasma beveling heads to create the weld grooves (V, X, or U-grooves) in a single pass, saving significant time.
Customization: Focus on high-precision cutting and integrated beveling capabilities to ensure excellent fit-up for the subsequent welding stages.
2) Plate Rolling
Here, the flat steel plates are formed into cylindrical or conical sections, known as "cans."
Equipment:
Four-Roll Plate Bending Machine: This is the industry standard for wind towers.
Customization: Choose a machine with the capacity to handle your maximum plate thickness and width. The four-roll design is superior for this application because it allows for pre-bending of the plate ends, which minimizes the un-rolled flat sections that would otherwise require manual rework.
3) Longitudinal Seam Welding
This is where the cylinder is formed by welding the single, long seam.
Equipment:
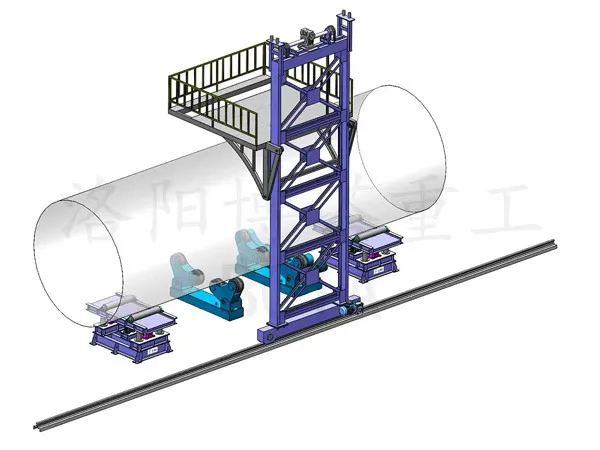
Welding Manipulator (Column and Boom) with a Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) Head: The column and boom system supports the welding head, while SAW is used for its high deposition rate and deep penetration.
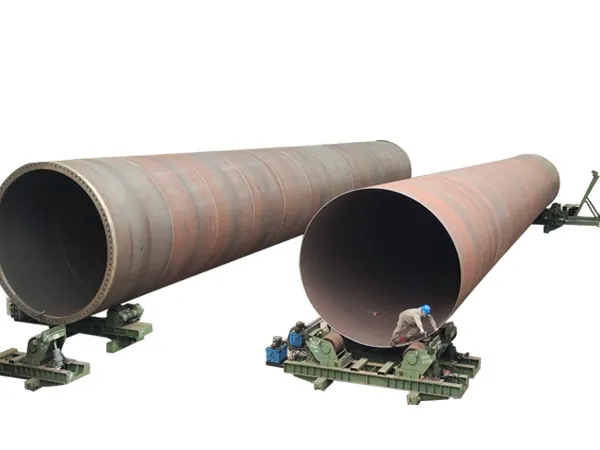
Welding Rotators: These rotate the cylinder to present the seam to the welding head.
Customization:
Automation: Implement laser seam tracking and automated controls to ensure the welding head stays perfectly aligned with the seam, especially for conical sections.
Welding Process: For high production volumes and thicker plates, consider using tandem or multi-wire SAW systems to increase deposition rates and reduce the number of passes required.
Welding Rotators: Use adjustable or self-aligning rotators to accommodate a range of cylinder diameters.
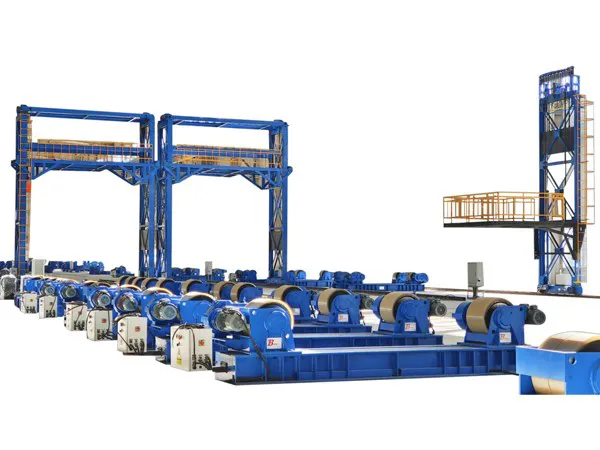

4) Fit-Up and Growing Line
In this stage, individual cans are joined together to form a longer tower section.
Equipment:
Hydraulic Fit-Up Rotators: These are essential for precisely aligning two large, heavy sections before they are welded. They use hydraulic cylinders to make fine height and angle adjustments.
Growing Line System: This integrated system combines fit-up rotators with a welding manipulator that can travel along the length of the growing tower section.
Customization: The "growing line" is one of the most important areas for customization. Select a system with a high capacity and advanced controls (like a PLC/HMI touchscreen) that allow operators to easily adjust for varying diameters and lengths.
5) Circumferential Seam Welding
This final welding stage joins the aligned tower sections.
Equipment:
Welding Manipulator: A large-scale column and boom system, often with tandem SAW heads.
Welding Rotators: Heavy-duty rotators to support and turn the growing tower section.
Customization: The level of automation here is key. Fully automated systems with real-time feedback and data logging can monitor and adjust welding parameters on the fly, ensuring consistent, high-quality welds and reducing defects.
No. 1 Intersection of Chuangye Avenue and Weilai Avenue,
Yiyang County,Luoyang City, Henan Province, China
+86 400-0379-069
Copyright © 2023 An Automated Welding and Cutting Equipment Manufacturer Focusing on Welding Column Boom and Welding Rotator | All Rights Reserved Technical support: ShangXian