Choosing a suitable wind tower welding production line is a complex process that depends on several key factors related to your production requirements, financial constraints, and site-specific conditions. The primary goal is to find a system that maximizes efficiency and quality while being cost-effective.
Before you even look at a single piece of equipment, you must clearly define your operational needs.
1. Production Capacity & Takt Time
Target Output: How many towers (or tower sections/cans) do you need to produce per week, month, or year? This is the single most important factor.
Takt Time: Calculate the maximum time allowed to produce one unit to meet demand. This will determine the required welding speed and level of automation.
Shift Patterns: How many shifts will you run per day? A two-shift operation needs a more robust and faster line than a single-shift operation for the same annual output.
2. Tower Specifications (Current & Future)
Diameter Range: What is the minimum and maximum diameter of the tower sections you will produce? This dictates the size of your rolling machines and turning rolls.
Plate Thickness Range: What are the minimum and maximum steel plate thicknesses? This determines the required power of the welding sources, the choice of welding process (e.g., single-wire SAW vs. tandem or multi-wire SAW), and the power of the plate rolling machine.
Section Length: What is the standard length of a single "can" or section? This influences the length of the welding manipulators and the workshop layout.
Material Type: What grade of steel will you be using (e.g., S355, S460)? Different materials have different welding requirements.
Future Trends: Are towers getting taller, thicker, or using higher-strength steel? Plan for the future. Buying a line that is maxed out on day one is a poor investment. Consider a 5-10 year outlook.
3. Workshop Layout & Logistics
Available Space: Map out your facility. Consider the footprint of the entire line, including space for plate storage, work-in-progress (WIP), and finished section storage.
Ceiling Height & Crane Capacity: Do your overhead cranes have sufficient height and lifting capacity to handle the largest and heaviest tower sections? This is a frequent bottleneck.
Material Flow: Design a logical, linear flow from raw plate delivery to finished section painting and shipping to minimize handling time and costs.
4. Desired Level of Automation
Manual: Operator-intensive, suitable for very low volume or custom work. Not recommended for modern tower production.
Semi-Automated: A mix of automated welding processes with manual setup and positioning. A common and flexible choice.
Fully Automated: Integrated systems with CNC control, automated material transfer, laser seam tracking, and data logging. Higher initial cost but delivers the best consistency, speed, and lowest labor cost per unit.

A typical wind tower production line is a series of specialized stations. Here’s what to look for in each.
1. Plate Preparation Station
Function: Cutting plates to size and creating the weld bevels (V, X, or U grooves).
Key Equipment: CNC Plasma/Oxy-fuel Cutting Machine with a milling or plasma beveling head.
Selection Criteria:
Precision: High-precision cutting is essential for good fit-up and weld quality.
Beveling Capability: The ability to create accurate, consistent bevels in a single pass saves enormous time.
Table Size: Must accommodate your largest plates.
2. Plate Rolling Machine
Function: Forming the flat plates into cylindrical or conical "cans."
Key Equipment: 4-Roll Plate Bending Machine.
Selection Criteria:
Capacity: Must be rated for your maximum plate thickness and width.
4-Roll vs. 3-Roll: A 4-roll machine is superior for tower production. It allows pre-bending of the plate ends, minimizing the flat-end section and requiring less follow-up work.
CNC Control: Essential for producing consistent diameters and cone shapes, reducing operator dependency and error.
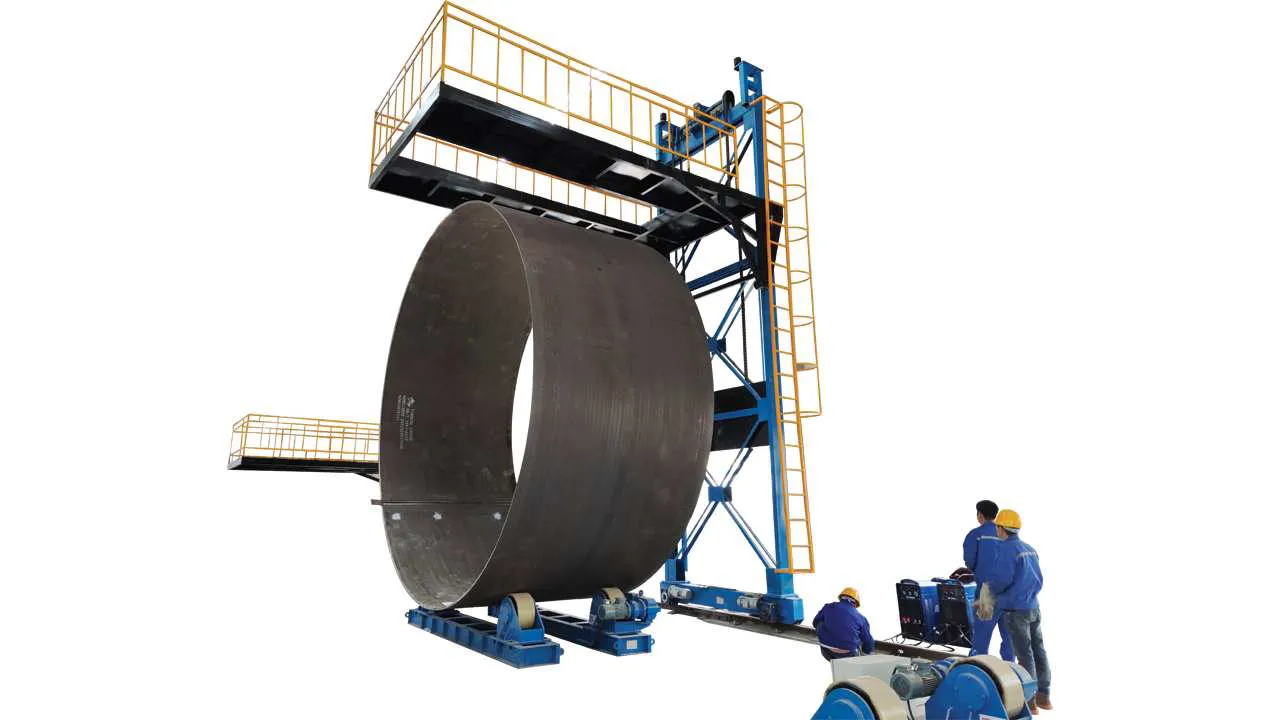
3. Longitudinal Seam Welding Station (L-Seam)
Function: Welding the single long seam to close the rolled can. This is often the production bottleneck.
Key Equipment: A system consisting of a welding manipulator (column & boom), a fit-up/alignment system, and a powerful welding power source.
Selection Criteria:
Welding Process: Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) is standard. For high productivity on thick plates (>25mm), consider Tandem-Wire or Multi-Wire SAW, which dramatically increases deposition rates.
Welding Manipulator: The column and boom must be extremely rigid to prevent vibration. Its reach and travel length must match your can dimensions.
Seam Tracking: Laser or tactile seam trackers are crucial for keeping the welding arc perfectly in the joint, ensuring consistent weld quality.
Flux Handling: An integrated flux recovery and feeding system is non-negotiable for efficiency and cost savings.
4. Can Fit-Up & Circumferential Seam Welding Station (C-Seam)
Function: Joining two or more cans together, or welding a flange to a can.
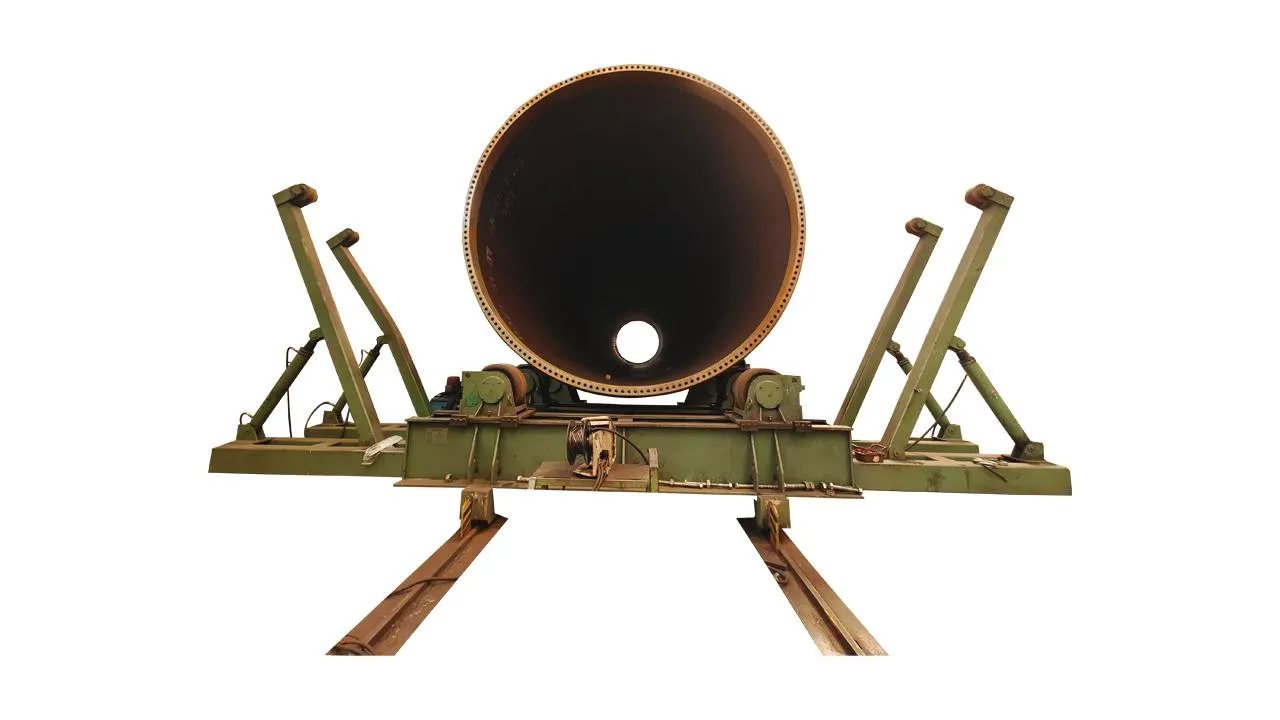
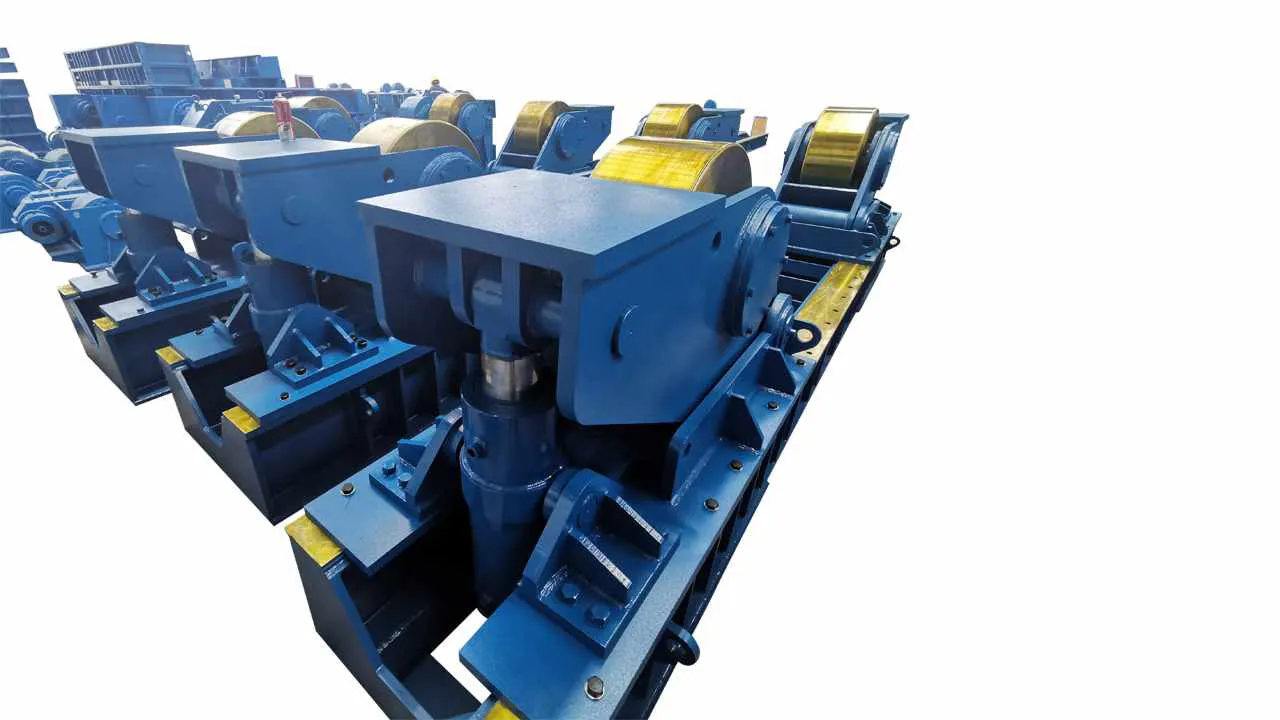
Key Equipment: A set of heavy-duty Turning Rolls (Rotators) and a Welding Manipulator.
Selection Criteria:
Turning Rolls:
Capacity: Must handle the total weight of the assembled tower section.
Synchronization: Drive units must be synchronized to ensure smooth, constant rotation without putting stress on the weld joint.
Alignment: Look for hydraulic or motorized systems on the rotators to help with the vertical and horizontal alignment (fit-up) of the cans. This is a massive time-saver.
Welding Manipulator: Same criteria as the L-Seam station, but often needs greater vertical and horizontal reach.
Fit-Up System: Dedicated hydraulic fit-up systems can press sections together to eliminate gaps before welding, which is critical for quality.
5. Flange & Detail Welding Station
Function: Welding the large flanges and door frames.
Key Equipment: Can be done at the C-Seam station or a dedicated station with welding positioners.
Selection Criteria: The welding head needs to be able to reach into the corner joint between the flange and the tower wall. Specialized manipulators or GMAW/FCAW (MIG welding) processes might be used here.

Choosing the right partner is as important as choosing the right equipment.
1. Experience & Reputation
Look for suppliers with a proven track record specifically in the wind tower industry.
Ask for a list of existing clients and installations. Contact these references.
2. Technical Capability & Customization
Can they design a line that fits your specific needs and workshop space?
Do they offer modern technology like advanced seam tracking, welding data monitoring (Industry 4.0), and remote diagnostics?
3. Service & Support: This is critical.
Installation & Commissioning: Do they provide a full turnkey installation?
Training: Is comprehensive operator and maintenance training included?
After-Sales Support: What is their response time for technical issues? Where are their service technicians located?
Spare Parts Availability: How quickly can you get critical spare parts? A line is useless if it's down waiting for a part.
4. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Don't just compare the initial purchase price.
Consider the long-term costs: energy consumption, consumables (wire, flux), maintenance, and potential downtime. A cheaper, less reliable machine will cost you far more in the long run.
5. On-Site Visit
If possible, visit the supplier's manufacturing facility to assess their quality and engineering capabilities.
Even better, visit an existing production line they have installed at another customer's facility to see it in action.
Summary Checklist:
Define Needs: Capacity, Tower Specs (now & future), Budget, Layout.
Identify Key Stations: Plate Prep, Rolling, L-Seam, C-Seam, Flange.Specify Equipment:
4-Roll CNC Plate Roller.
High-Deposition SAW process (e.g., Tandem Wire).
Rigid Column & Boom with Laser Seam Tracking.
Heavy-Duty, Synchronized Turning Rolls with integrated fit-up.
Automated Flux Handling.
Shortlist Suppliers: Based on wind industry experience.
Request Detailed Proposals: Compare not just price, but technology, quality of components, and support.
Check References & Visit Sites.
Negotiate: Focus on TCO, warranty, and service level agreements (SLAs).
By following this structured process, you will be well-equipped to select a wind tower welding production line that is not only suitable for today but is also a robust and profitable asset for years to come.
No. 1 Intersection of Chuangye Avenue and Weilai Avenue,
Yiyang County,Luoyang City, Henan Province, China
+86 400-0379-069
Copyright © 2023 An Automated Welding and Cutting Equipment Manufacturer Focusing on Welding Column Boom and Welding Rotator | All Rights Reserved Technical support: ShangXian